Securing a bank loan can be a significant step for any business, providing much-needed capital for growth and expansion. However, accurately recording the bank loan transaction in your accounting system is crucial for maintaining financial transparency and understanding your company’s true financial position.
In Short: To record Bank Loan Journal Entry, you’ll use a simple journal entry involving two accounts: Cash (Debit) and Loan Payable (Credit).
Understanding the Basics
A bank loan represents a liability for your business. It’s essentially borrowed money that must be repaid with interest over a set period. The initial receipt of the loan increases your cash balance (an asset), while the obligation to repay the loan creates a liability on your balance sheet.
The Bank Loan Journal Entry
Here’s how to record the initial receipt of a bank loan in your accounting system:
Step 1: Identify the accounts involved:
- Cash (Debit): This account increases to reflect the received loan amount.
- Loan Payable (Credit): This account represents the liability created by the loan.
Step 2: Understand the debit and credit sides:
- Debit: Increases asset accounts (cash).
- Credit: Increases liability accounts (loan payable).
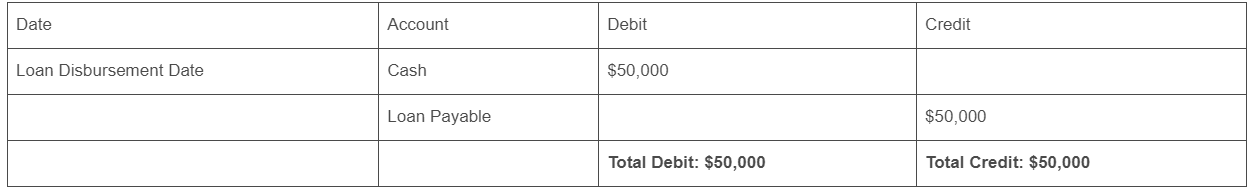
Step 3: Example Journal Entry:
Let’s say you receive a $50,000 loan from the bank. The journal entry would look like this:
Debit: Cash $50,000
Credit: Loan Payable $50,000
Recording Interest Payments
As you make interest payments on the loan, you’ll need to record them separately:
Step 1: Identify the accounts involved:
- Interest Expense (Debit): This account reflects the cost of borrowing money.
- Cash (Credit): This account decreases as you pay the interest.
Step 2: Determine the interest amount:
- This will typically be calculated based on the loan’s interest rate and principal balance.
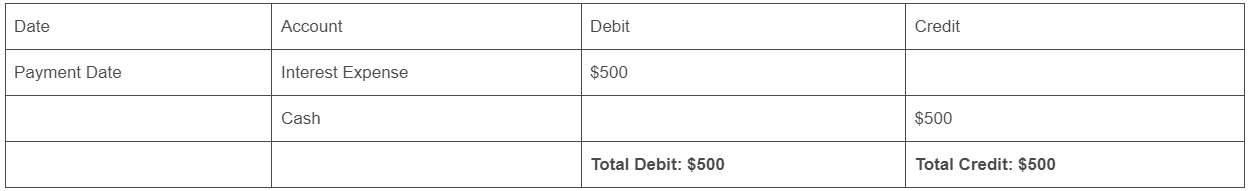
Step 3: Example Journal Entry (for monthly interest payment of $500):
Debit: Interest Expense $500
Credit: Cash $500
Check Out: How to Record Bank Overdraft Journal Entry: A Step-by-Step Guide
Tips for Accurate Recording
- Keep all loan documents, including the loan agreement, in a safe place.
- Use dedicated accounting software to easily track loan payments and interest accrual.
- Regularly reconcile your bank statements with your loan account records.
Conclusion
Accurately recording bank loans is essential for maintaining transparent financial records. By understanding the journal entry process and consistently tracking payments and interest accruals, you can ensure your financial statements reflect your company’s true financial health, including its debt obligations.
FAQs:
- What if I receive a loan with a variable interest rate? You’ll need to adjust your interest expense recording each period based on the current rate.
- How do I record loan principal repayments? Debit loan payable and credit cash for the amount of principal repaid.
- Can I deduct interest expense on my taxes? Consult a tax professional for specific guidance, as interest expense is often deductible for tax purposes.
By diligently tracking your bank loans and related transactions, you can gain a clearer picture of your financial position and make informed decisions about your business’s future.
Helpful Resources:
Bank Loans: What Is a Loan, How Does It Work, Types, and Tips on Getting One
Accounting for Liabilities: AccountingTools article
Small Business Loan Options: Small Business Administration
Tax Implications of Interest Expense: IRS publication