A Bank Overdraft Journal Entry occurs when you spend more money than you have in your account. It’s a situation most businesses want to avoid, but sometimes it happens due to unexpected expenses or errors in tracking. Understanding how to record a bank overdraft in your accounting system is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring your financial statements reflect your true financial position.
In Short: To record Bank Overdraft, you’ll use a simple journal entry involving two accounts: Overdraft Fee Expense (Debit) and Overdraft Payable (Credit).
Understanding the Basics of Bank Overdraft Journal Entry
A bank overdraft creates a liability for your business. It means you owe money to the bank for exceeding your account balance. This liability typically comes with fees and penalties, which further add to your financial burden.
The Bank Overdraft Journal Entry
Recording a bank overdraft involves a simple journal entry:
Step 1: Identify the accounts involved:
- Overdraft Fee Expense (Debit): This account reflects the cost of the overdraft fee charged by the bank.
- Overdraft Payable (Credit): This account represents the liability created by the overdraft.
Step 2: Understand the debit and credit sides:
- Debit: Increases expense accounts (overdraft fee expense).
- Credit: Increases liability accounts (overdraft payable).
Step 3: Example Journal Entry (assuming a $35 overdraft fee):
Debit: Overdraft fee expense $35
Credit Overdraft Payable $35

Important Note: You’ll also need to adjust your cash balance to reflect the overdraft amount. This is typically done by directly reducing your cash account balance in your accounting system.
Reconciling the Overdraft
Once you have sufficient funds in your account, you’ll need to repay the overdraft balance and any associated fees. This is recorded as follows:
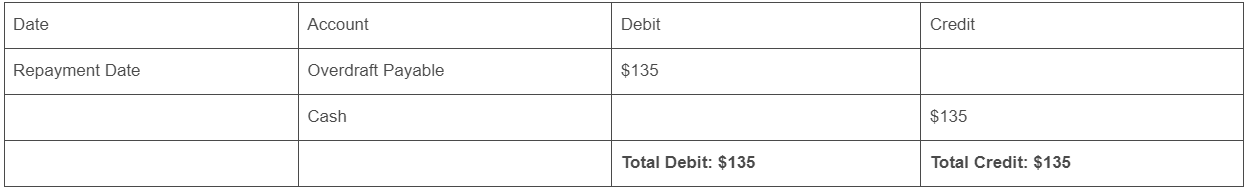
Step 1: Identify the accounts involved:
- Overdraft Payable (Debit): This account decreases as you repay the liability.
- Cash (Credit): This account decreases as you pay the overdraft balance.
Step 2: Determine the repayment amount:
- This will include the overdraft balance and any fees owed.
Step 3: Example Journal Entry (assuming an overdraft balance of $100):
Tips for Avoiding Overdrafts
- Track your account balance carefully and set up alerts for low balances.
- Reconcile your bank statements regularly to identify any discrepancies.
- Consider using a budgeting system to manage your spending.
Conclusion to Bank Overdraft Journal Entry
While bank overdrafts are a situation to avoid, understanding how to record them in your accounting system is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records. By promptly recording the overdraft expense and liability, and then accurately tracking the repayment, you ensure your financial statements provide a clear picture of your company’s true financial position.
FAQs:
- Do overdraft fees vary between banks? Yes, fees can vary depending on the bank and the type of account.
- Can I negotiate overdraft fees? It’s worth trying to negotiate with your bank, but they may not be willing to waive or reduce the fees.
- What if I can’t immediately repay the overdraft? Contact your bank to discuss options, as they may offer a payment plan or temporary loan.
- What is the journal entry for a bank overdraft?
bank overdraft occurs when a business or individual withdraws more money from their bank account than is available, resulting in a negative balance. The journal entry to record an overdraft involves:
Debit: Bank Account (for the overdraft amount) This represents the bank account becoming negative or overdrawn.
Credit: Bank Overdraft Liability (or an equivalent liability account) This reflects the obligation to repay the overdraft to the bank. - How does a bank overdraft affect the balance sheet?
On the balance sheet, a bank overdraft is considered a current liability, as it represents money owed to the bank that needs to be repaid in the short term.
Bank Overdraft Liability (Current Liability) increases on the liabilities side.
Bank Account (Asset) decreases or may show a negative balance.
In this way, the balance sheet reflects both the reduction in cash and the obligation to repay the overdraft.
Effect on Balance Sheet:
Assets: Cash/Bank decreases (negative balance).
Liabilities: Current liabilities increase by the overdraft amount. - Is a bank overdraft a debit or credit?
A bank overdraft is a credit to the bank account (because it increases the liability), but it’s recorded as a debit to the Bank Overdraft Liability account.
Debit: Bank Account (for the overdraft amount, showing a decrease in available funds)
Credit: Bank Overdraft Liability (to record the liability to the bank)
In summary:
Bank Overdraft is a credit in the bank account but results in a debit to the liability account (if you’re recording the liability to the bank).
By proactively managing your cash flow and preventing overdrafts, you can save yourself unnecessary financial stress and keep your business running smoothly.